Successful businesses don’t get where they are by accident. Even if a company’s backstory is filled with tales of visionary founders, risk-taking, and a fantastic product or service, there is probably someone paying close attention to the data behind the scenes.
Financial performance indicators help you to understand your company’s performance, including profitability, efficiency, successes, strengths, and weaknesses. This helps you to make more strategic decisions. This article runs through seven indicators to keep a close eye on.
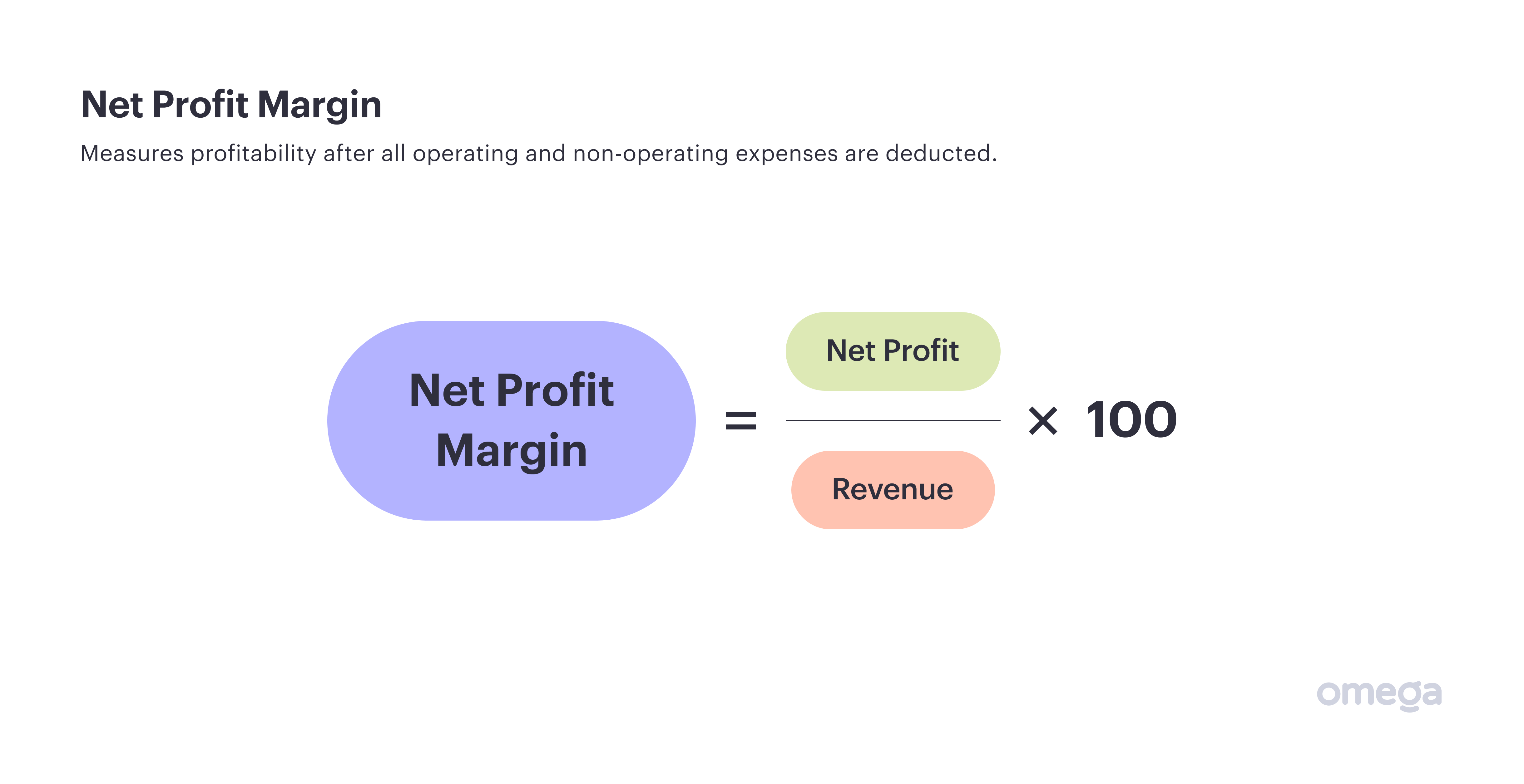
1. Net Profit Margin
Profitability is one of the most basic measures of a company’s success. By determining the revenue brought in after deducting expenses, you can see how sustainable a business is.
Net profit margin deducts both operating and non-operating expenses from profit, which builds a complete picture of a firm’s performance. Operating expenses encompass direct expenses like rent and utilities, while non-operating expenses include entries like taxes too.
This differs slightly from the gross profit margin — widely known as “profit margin” — which only considers operating expenses.
2. Sales Growth Rate
Even if you have a strong net profit margin, it will likely still be challenging to run a sustainable business without steady growth of sales. This is an indicator that your company is still enjoying healthy growth and bringing in new customers or sales.
Use the following formula:
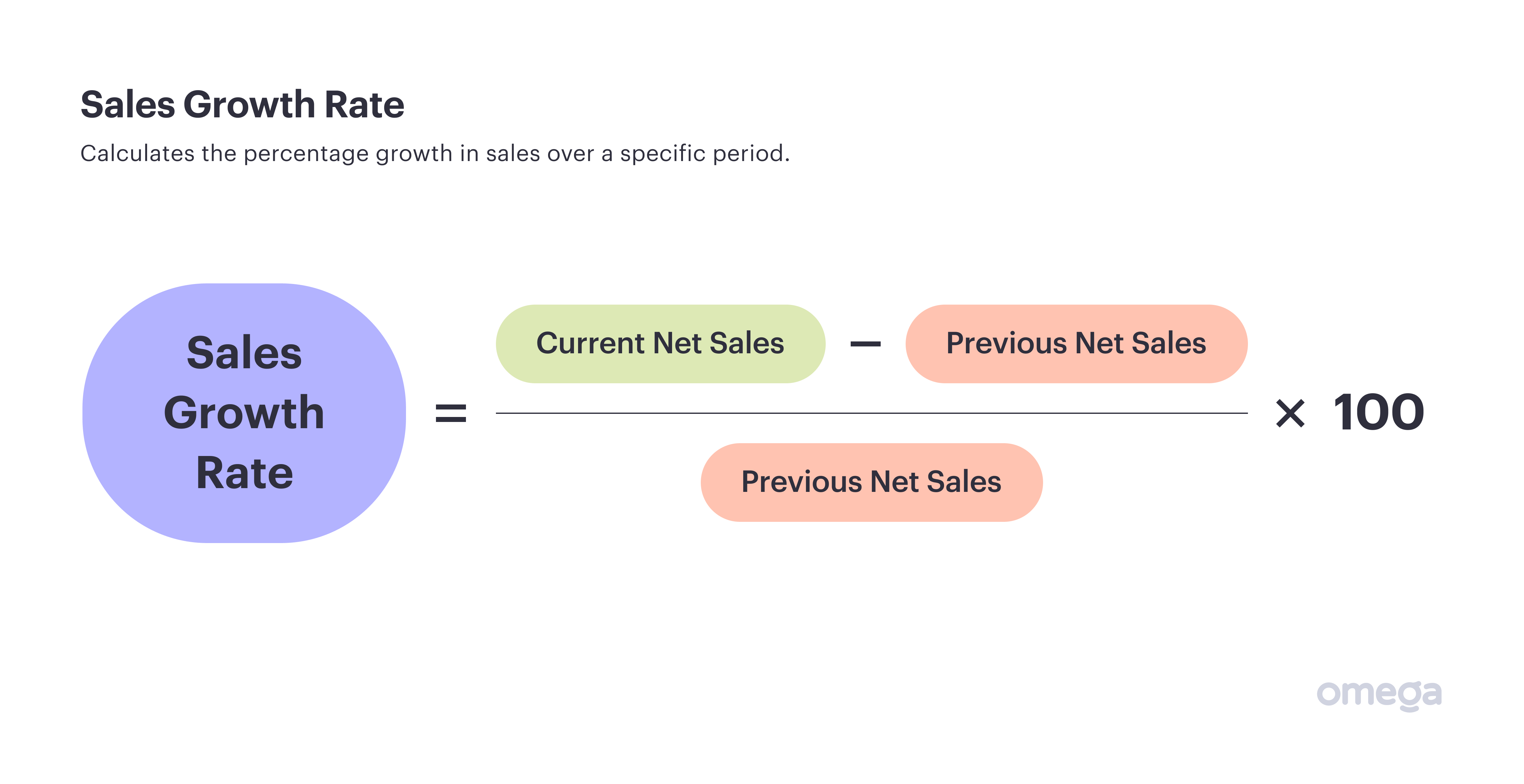
This results in a percentage — and the higher the rate, the better the growth.
3. Debt to Equity Ratio
When businesses pursue growth, they often take out debt to help them reach their goals faster, using it to fund equipment, production, staff, and more. While it’s not necessary for businesses to avoid debt completely, relying on it too much can lead to excessive risk and even insolvency.
Considering that the UK’s “business death rate” was 11.8% in 2022, this fate is a real possibility.
The debt to equity ratio helps companies to track their financial leverage so they can ensure they’re using debt responsibly. Debt includes all liabilities, while equity is the value in the company invested by owners and shareholders.
To calculate the ratio, simply divide total liabilities by shareholders’ equity.
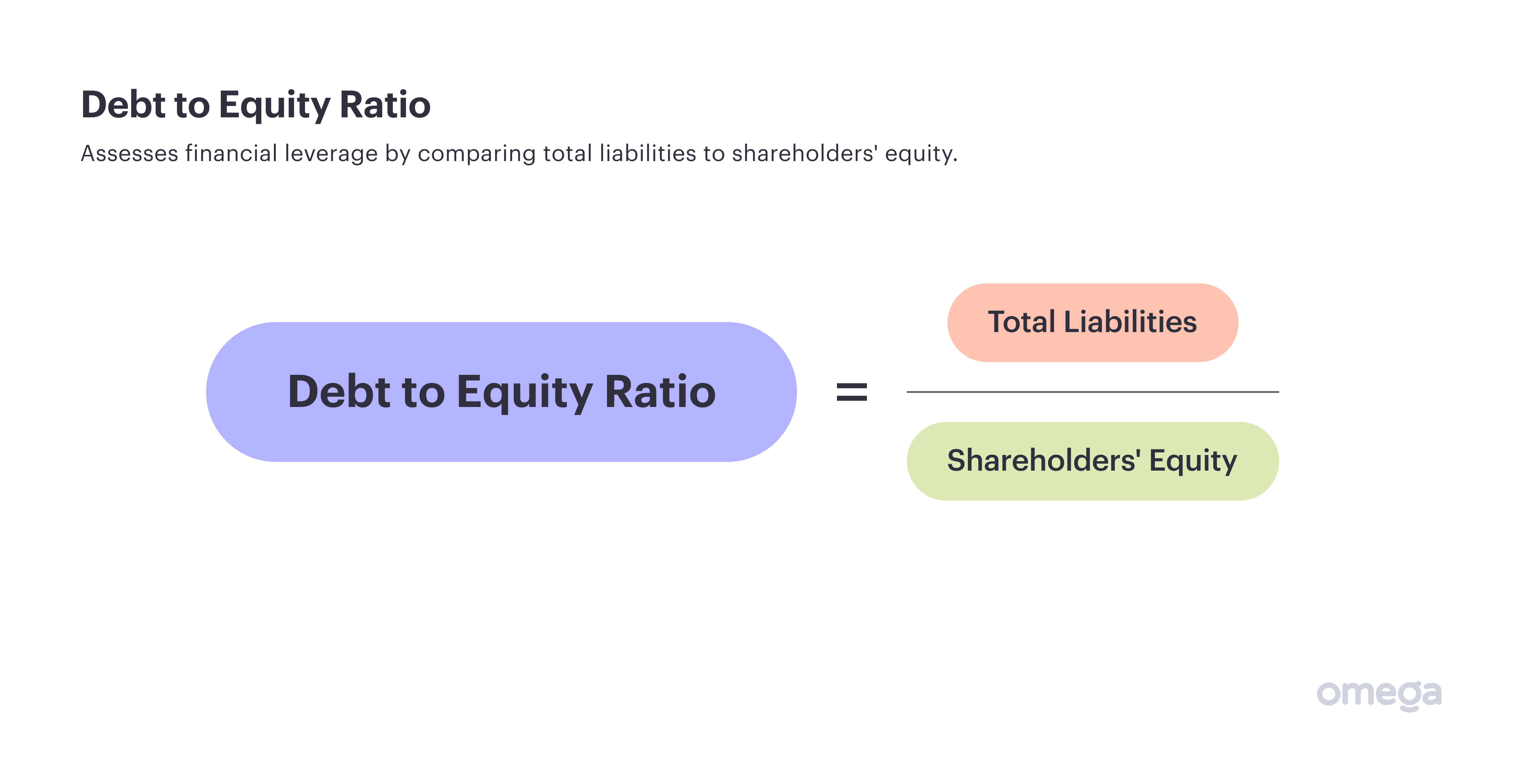
A lower number means you will be in a better position to apply for financing.
4. Customer Lifetime Value
Customers are the lifeblood of any business, but what kind of people is your business attracting? Do you have a lineup of loyal clients who make repeat purchases, or are there more people who make a single purchase and never return?
These are the kinds of questions that customer lifetime value aims to answer.
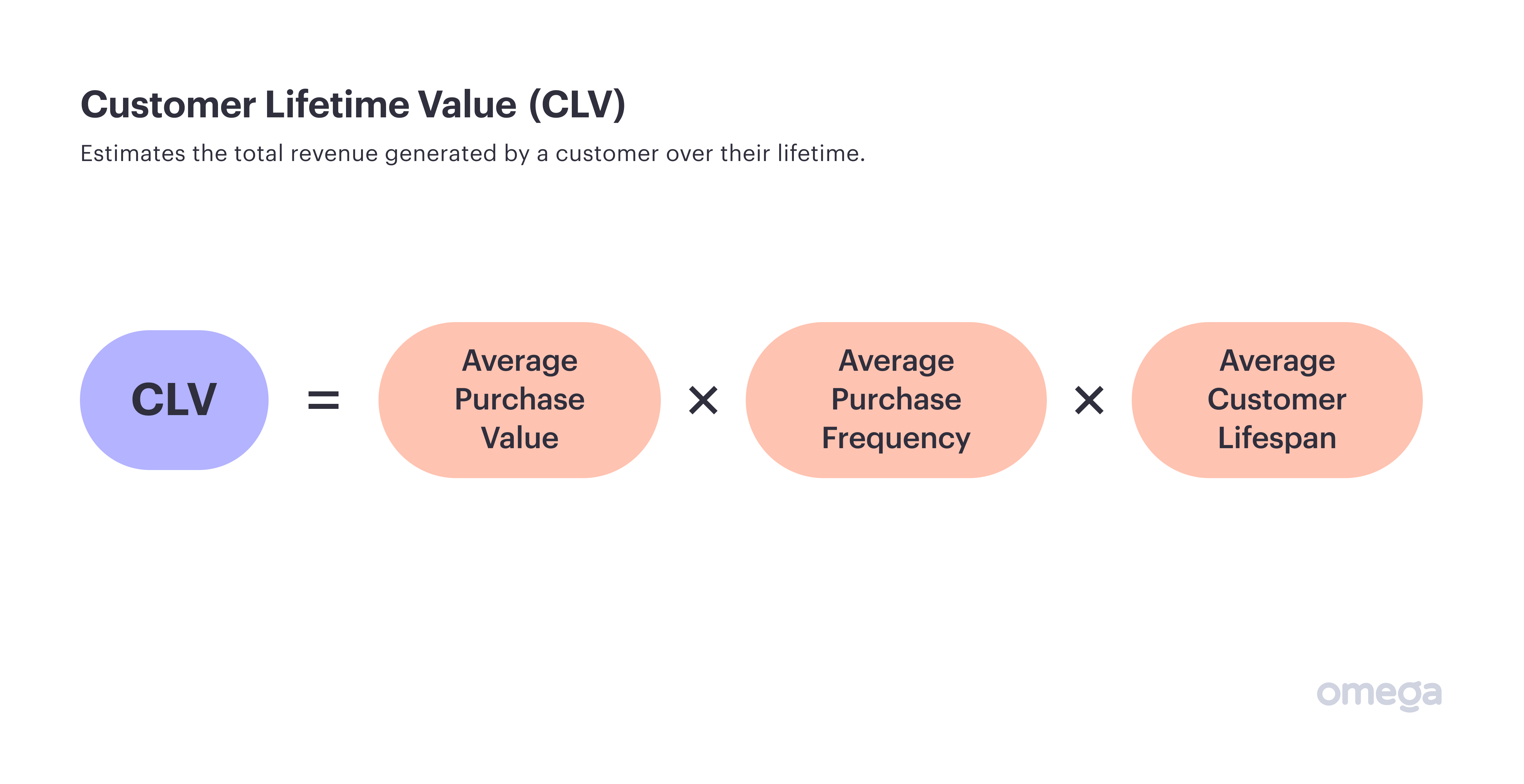
The metric estimates the revenue an individual customer represents. Estimate it by multiplying together the average purchase value, average purchase frequency, and average customer lifespan.
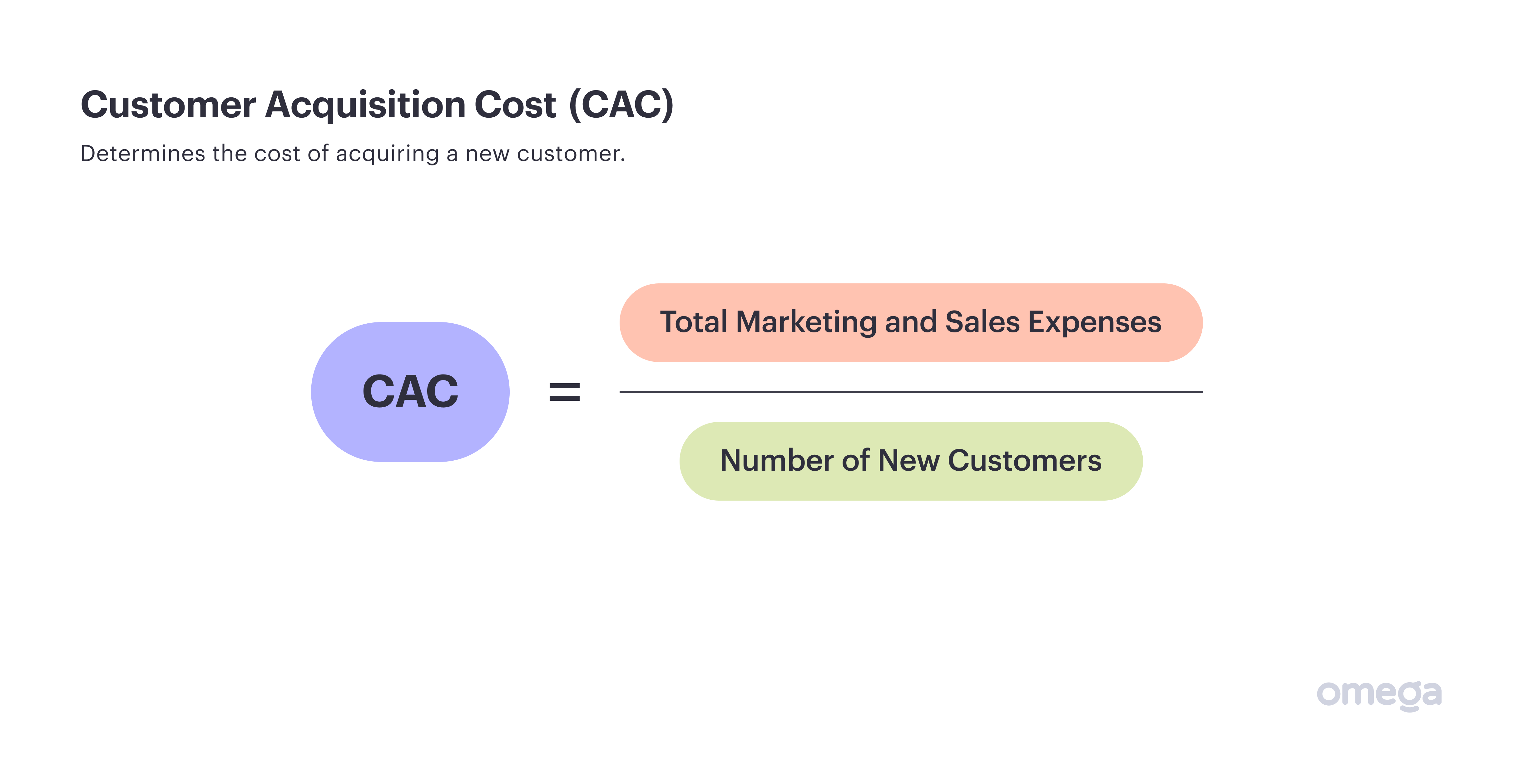
5. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customers are often hard to win and easy to lose. But exactly how hard are they to win? This is what CAC reveals by showing how much you spend on acquiring a new client.
You can calculate this by adding up everything you’re spending on marketing and sales, then dividing it by how many new customers you’re bringing in.
If you have a high CAC, it is not necessarily a bad thing as long as customers have a high lifetime value and you have a good retention rate.
6. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS takes a deeper dive into the area of profitability and expenses. It calculates the cost of making and selling products, therefore revealing if there’s any scope to reduce them and therefore boost efficiency (and profit).
This metric is mostly used by companies who hold a physical inventory, but can also be used by other firms.
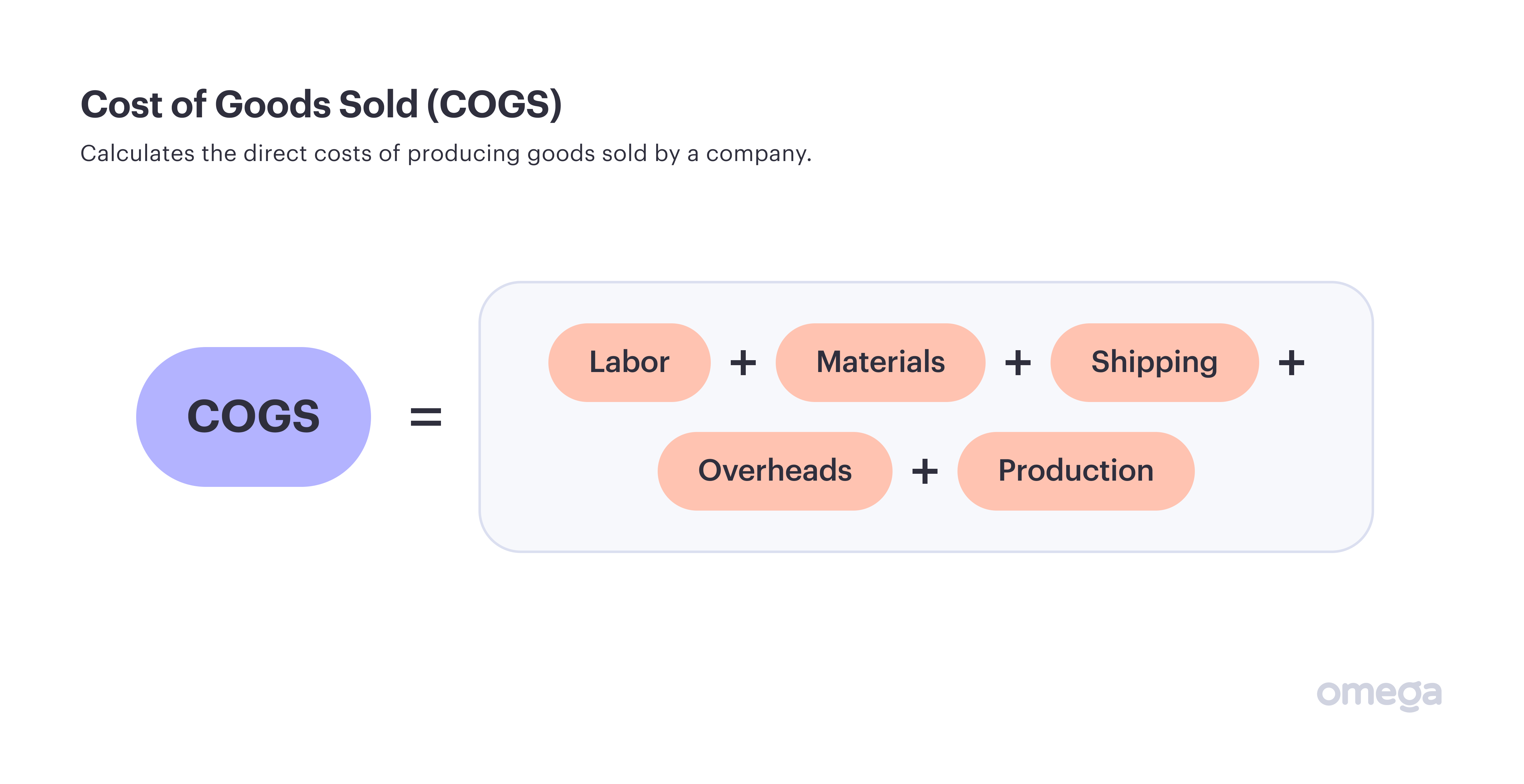
To calculate it, you need to work out direct costs. These include:
- Labour
- Materials
- Shipping
- Overheads
- Production
Meanwhile, indirect costs such as marketing and administration are excluded.
7. Accounts Receivable Turnover
Liquidity is one of the most important financial considerations for any business — without it, firms can find themselves unable to pay their bills. In 2022, SMEs were owed £22,000 in late payments on average, which can have a major impact on financial health.
The accounts receivable turnover is one useful metric related to liquidity, as it estimates the efficiency of collecting payments from clients.
Work it out by using the following formula:
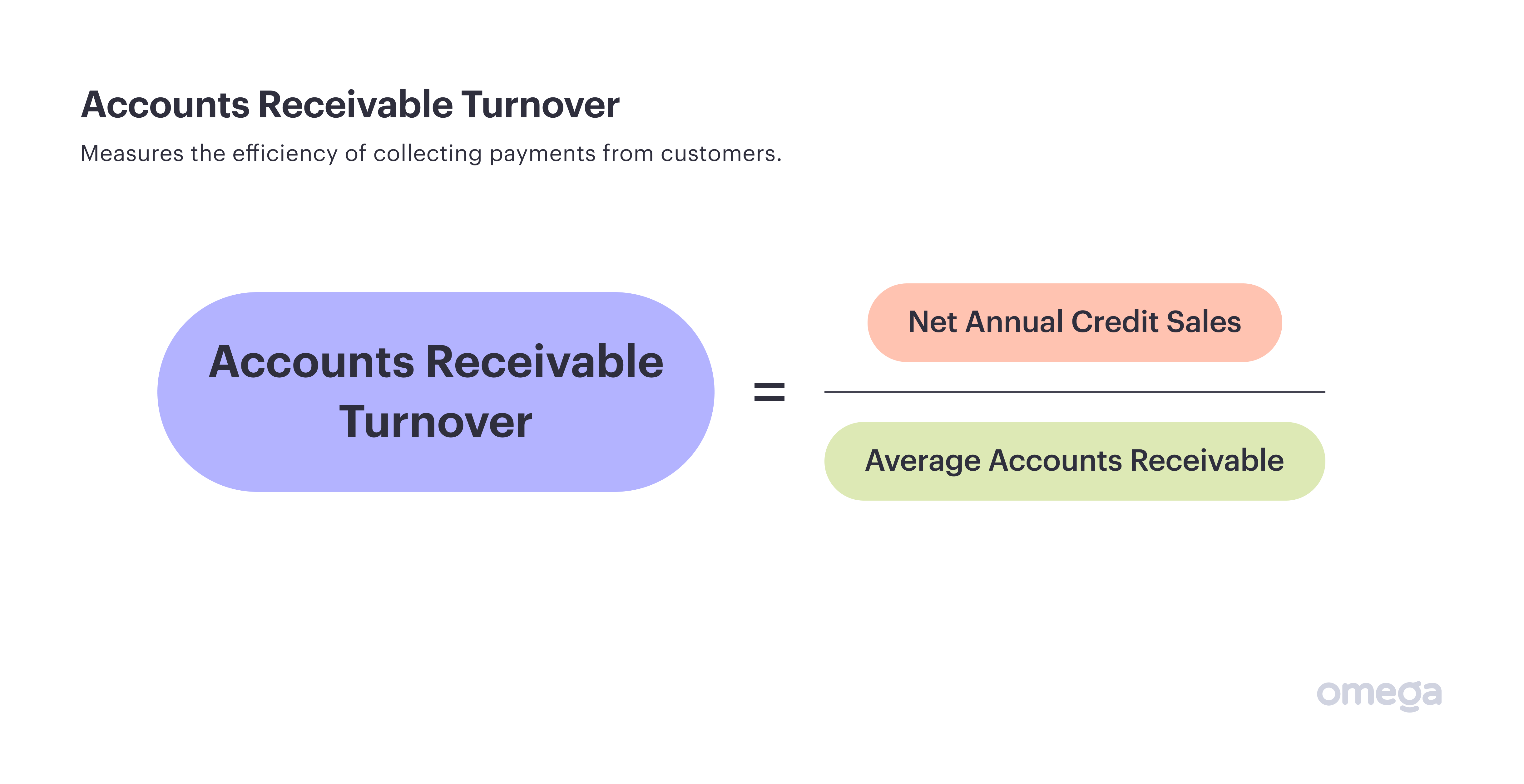
You can calculate credit sales by subtracting the payments you are owed by your completed payments. Meanwhile, calculate average accounts receivable by working out the difference in accounts receivable at the start and end of your desired period, then dividing it by two.
Time to Track
Analysing numbers on a spreadsheet might not be everyone’s favourite part of running a company, but without it, things can go wrong quickly. From customer acquisition cost to sales growth rate, the financial performance indicators outlined above will help you to stay ahead of the curve and make informed choices.
Looking for the perfect partner to run your business with? Omega is a financial management tools and services that provides what we call a “Business-in-a-Box” — a perfect suite of financial management tools and services in one platform.
Sound interesting? Get started on Omega today by completing your application.




