As the world becomes increasingly interconnected through the forces of globalisation, international entrepreneurs now face new challenges.
Working with overseas clients and suppliers means dealing with foreign currencies, and this can make even the most experienced business person break out in a cold sweat. After all, the instability of fluctuating currencies can cause chaos, especially when you are trying to move your company towards growth.
Thankfully, there is a way to reduce the risks, and that starts with understanding what affects the prices of financial instruments. Why do exchange rates fluctuate, and what causes this volatility? Let’s examine the factors influencing foreign exchange rates, which will help you plan your trades strategically.
1. Inflation
When inflation rises, goods and services become more expensive. But the effects of inflation don’t stop with shoppers feeling the pinch on their wallets. Prices going up means a decrease in the purchasing power of money, so countries with consistently low inflation rates will have currencies with a higher value (compared to countries with high inflation).
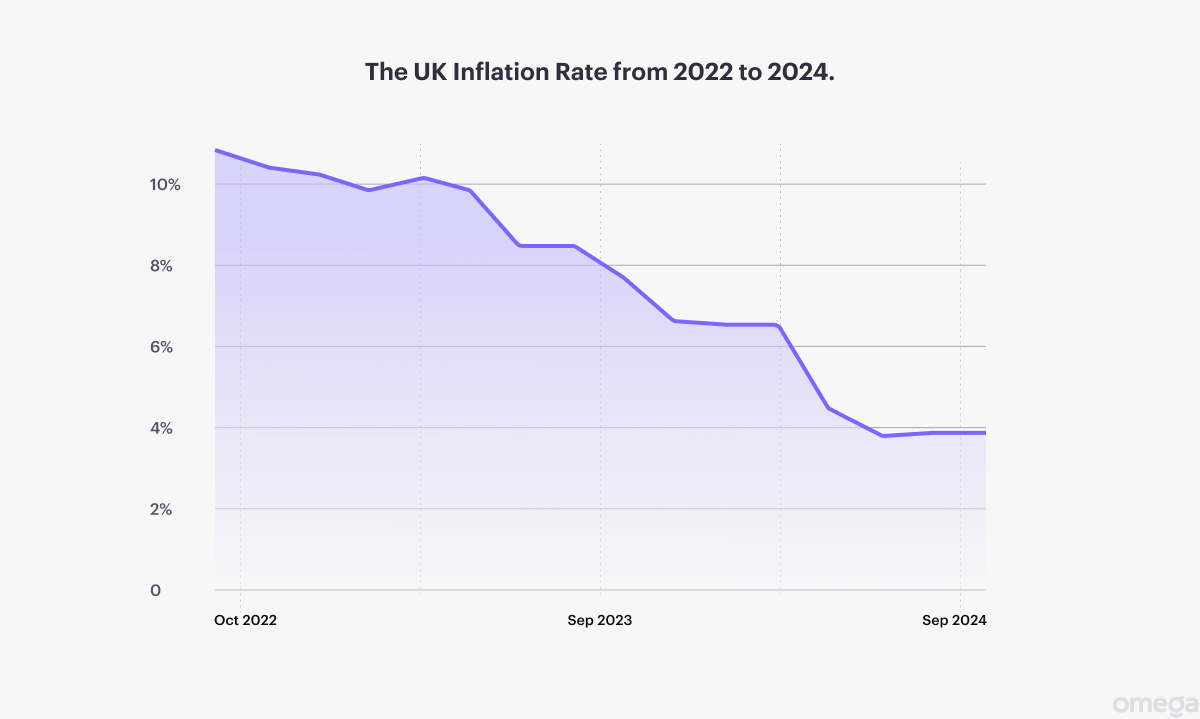
If you find this confusing, it may be helpful to remember that inflation and interest rates have an inverse relationship, meaning higher inflation decreases the value of a currency.
In August 2024, the annual inflation in the UK steadied at 2.2%. Experts have mixed views on whether the pound’s value will decrease or increase. Some expect that rate cuts from the Bank of England in 2024 could further weaken the pound.
2. Interest rates
Another major factor causing exchange rates to change is interest rates. There is only so much central banks and governments can do to curb rising inflation and maintain a steady economy. One solution is to increase interest rates, which consequently affects exchange rates.
Typically, the higher the interest rate, the more attractive the currency offer becomes to investors.
3. Economic indicators
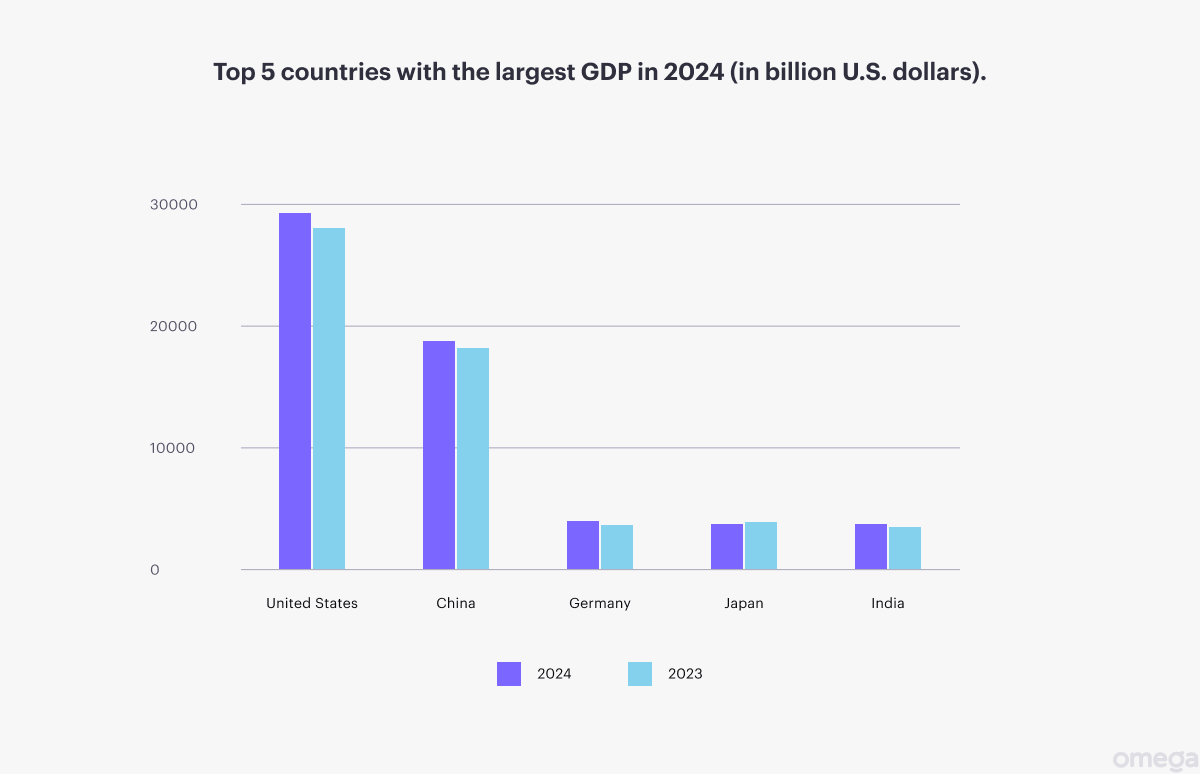
It is not only interest rates and inflation that determine the foreign exchange rate. It is also wise to look at Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which gives insight into the economic conditions of a country, including government debt, unemployment, and other important factors.
Fast GDP growth typically implies a strong economy. This increases demand for the country’s currency and consequently drives its value up.
It is also important to consider a country’s political environment, as this can influence exchange rates. When there is a political turmoil, it can reduce a country’s appeal to foreign capital, and therefore, the exchange rate of its currency may decline.
4. Government debt
Among the many exchange rate factors is the total national or public debt owed by the central government. Although public sector projects often require large-scale financing, a country with a large debt is less likely to attract foreign investors.
Moreover, in some cases, foreign investors might sell their bonds if an increase in government debt is expected. The result? An oversupply of the local currency and, therefore, a decrease in its value.
Other factors influencing foreign exchange rates you should pay attention to:
- Terms of trade.
- Safe haven status.
- Market sentiment.
- Current account deficits.
- Stock markets.
- Government intervention.
Final thoughts
It is not easy to predict changes in the economic market. But if you monitor these factors alongside current exchange rates, you’ll be able to make more informed decisions for your business.
At the end of the day, it’s important to remember that volatility is not always bad. If you have the right tools, you can develop a proper risk management strategy that makes it work to your advantage.
Interested in learning more about operating a UK business? Take a look at our other articles here.
Disclaimer.