Starting a business in the UK requires careful consideration of tax implications, legal status, and operational integrity. You don’t want to launch a company with the wrong structure and run into regulatory issues or excessive taxes that make thriving in the coming years much more challenging.
One of the key questions to ask your team is how a sole trader vs limited company applies to your business. Knowing how to structure your company and the different advantages and differences ensures you get a solid outcome that helps you grow and respond to market changes in the future.
Here are some of the differences between a sole trader and a limited company so that when it comes to filling in the required information and applying for legal status, you’re well equipped to make a decision.
What is a Sole Trader?

The question of sole trader or limited company begins with an understanding of each. A sole trader is better known as an individual who wants to own and operate any business. They are the single proprietors, answering no one else but themselves.
In many ways, this is helpful because there is far less “red tape” to cut through when making decisions. You get a little more flexibility when the team meetings consist of yourself in a coffee shop with a blank page of paper and no one else.
- Full Control: You get complete control over any decision-making process, which is a significant difference between sole trader and limited company structures.
- Simple Setup: One of the advantages of being a sole trader is that the complexity of start-up costs, paperwork and general bureaucracy is much simpler and is often listed in the advantages of being a sole trader.
- Tax Efficiency: Taxes vary based on the region you set up your business structure, but in general, you pay personal income tax on profits instead of as a corporation or larger entity.
You will find plenty of support with services through Omega. Having global payments and multi-currency accounts allows you to engage in international trade with the same flexibility and scalability you would expect by being the only person accountable for decision making.
What is a Limited Company?

When asking, “should I be a sole trader or limited company?” you also want to consider the structure’s popularity. There are well over 5 million limited companies in the UK alone, making it one of the most well-known entities for international trading.
A limited company is separate from the owners. It is its own legal entity. Shareholders might run the company, but there is a “shield” of legal protection where personal assets are protected from business liabilities. This structure helps minimise personal risk, and business assets like government support and bank startup loans are available.

- Limited Liability: One of the best benefits of a limited company over a sole trader is the protection it offers. You are not personally responsible for any debts or risks in this structure.
- Prestige: When you commit to a limited company, you put a professional image on your brand, establishing your company as a leader and not a single person.
- Tax Advantages: Limited companies have more tax efficient structures where profits and rates can be changed based on deductions, incentives, and other government benefits.
- Raising Capital: It is far more efficient to receive funding, angel investing, and government loans when you have a formal limited company structure.
Using Omega’s Business-in-a-Box service provides you with a team already well-versed in crafting limited companies. Everything from company registration services to legal and accounting is managed on your behalf so you can focus on what matters most – growing profits and customer relationships.
Difference Between Sole Trader and Private Limited Company
You will find many differences between a sole trader entity and a limited company. For one, the liability shield is extremely different. When you operate as a sole trader, you run the risk of having personal assets open to lawsuits and damages. A limited company provides a shield where only the legally recognised assets of the company are at risk.
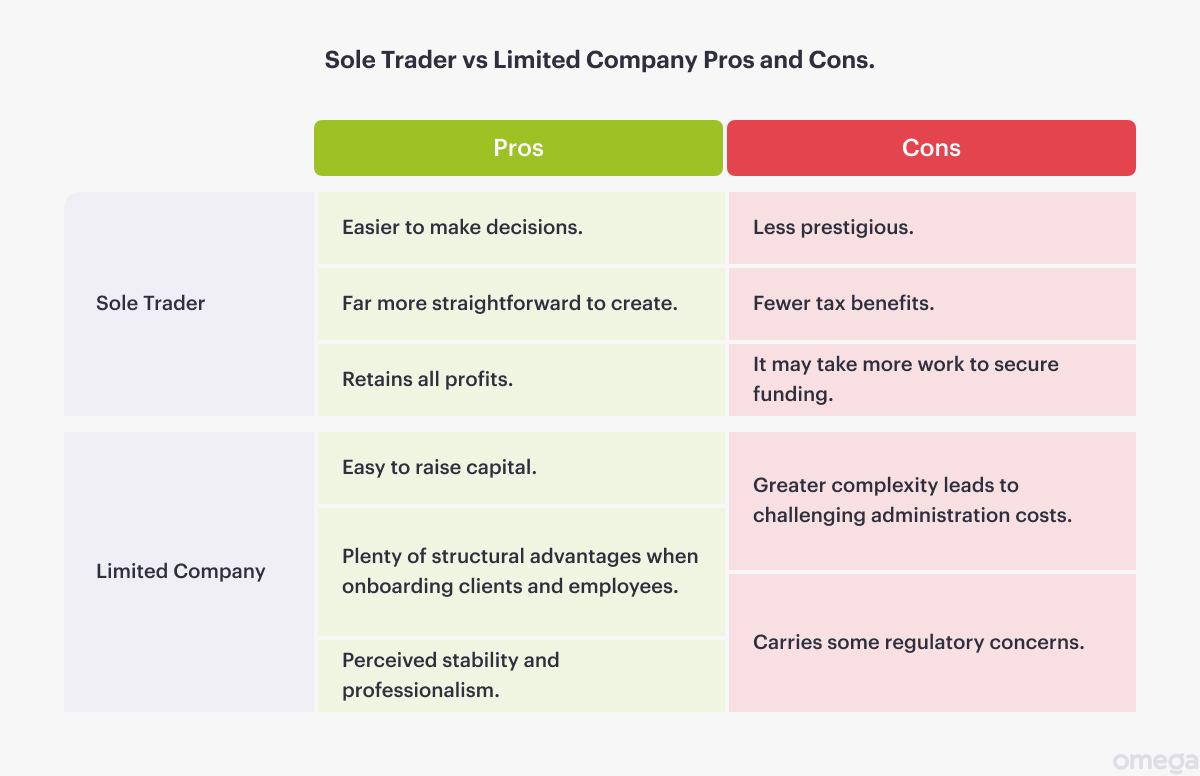
Taxation will also change. Running a sole trader business is like having your own profits. There is no corporate structure. While you get way more flexibility and control over every decision, you are also responsible for all profits without as many deductions or incentives from a formal limited company.
Finally, a business’s prestigious “face” often rests on its reputation. When you meet all the administrative requirements of being a limited company, you get a stronger professional presence that other international traders will appreciate. The only way to get the same for a sole trader is by building a network of clients and slowly establishing yourself as a financial juggernaut in the industry.
FAQs
Final Thoughts
Deciding to secure a sole trader or limited company is entirely up to you and your team. Be sure to look at what types of taxes you envision paying, how you want assets protected, and what flexibility you want in decision making.
Once you have decided, use Omega’s Business-in-a-Box to set up the necessary structure so you can save time, money, and stress over making international business transactions. Whether you are an up and coming sole trader or looking to expand into a limited company, Omega has the tools and services to help you thrive.
Disclaimer.




